在现代软件开发中,规范的提交信息不仅是一种最佳实践,更是提升团队协作效率和项目可维护性的关键要素。AI 辅助提交(AI Commits)技术通过智能分析代码差异和上下文,自动生成符合规范的提交信息,让开发人员从繁琐的格式规范中解放出来,更专注于核心逻辑的实现。
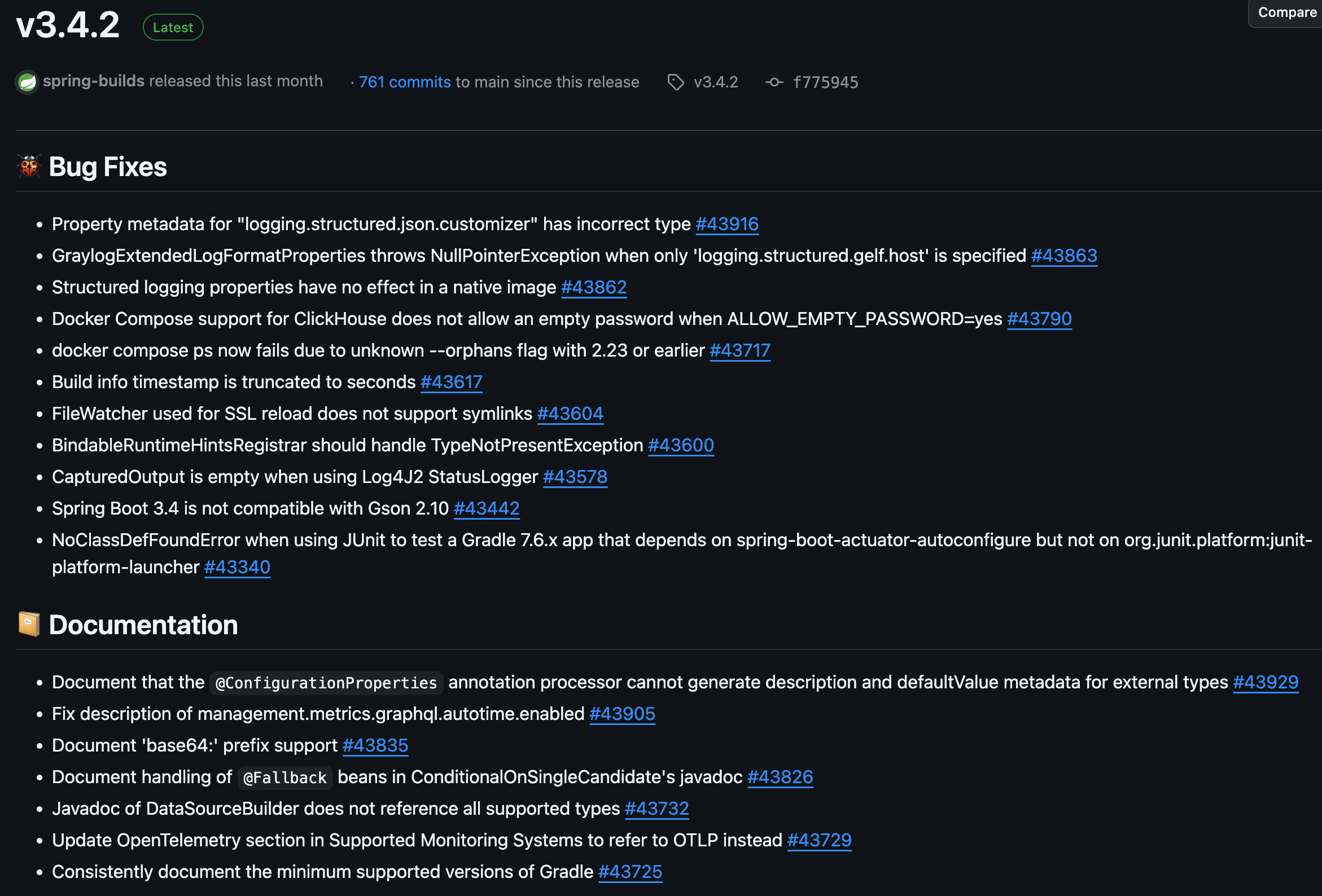
以 spring-boot项目 release 为例,高质量的提交信息,可以自动化生成 release log。
一、Git 提交规范基础
1.1 Conventional Commits 规范介绍
Conventional Commits 是一种广泛使用的 Git 提交信息规范,它通过简单的格式约定让提交信息更加清晰易懂。这个规范最初由 Angular 团队提出,现已成为开源社区的事实标准(规范详情)。
采用这个规范的主要好处是:
- 提交历史更加清晰,方便团队成员快速了解代码变更
- 可以自动生成版本更新日志(Changelog)
- 根据提交类型自动判断版本号变化
- 便于代码审查,审查者能快速理解变更意图
1.2 基本格式与组成
标准的提交信息格式如下:
<type>(<scope>): <description>
[optional body]
[optional footer(s)]
-
type: 必选,表示提交类型
- feat: 新功能
- fix: 修复bug
- docs: 文档更新
- style: 代码格式(不影响代码运行的变动)
- refactor: 重构
- test: 测试相关
- chore: 构建过程或辅助工具的变动
-
scope: 可选,表示影响范围,如模块名称
-
description: 必选,简短描述,使用祈使语气
-
body: 可选,详细说明
-
footer: 可选,用于说明重大变更(BREAKING CHANGE)或关闭 Issue
笔者团队使用 Conventional Commits 规范提交信息,效果如下:

二、AI Commits 技术实现
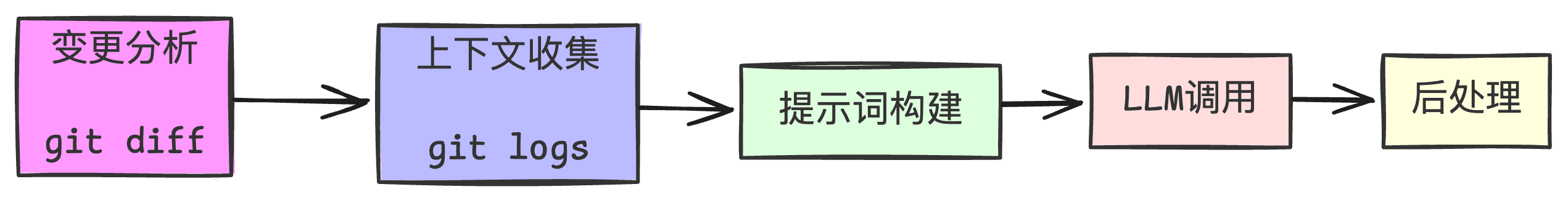 我们通过分析开源项目 aicommits-shell(Shell实现版本)的代码实现,深入解析AI生成Git提交信息的核心工作流程。
AI Commits 的核心工作流程包含以下步骤:
我们通过分析开源项目 aicommits-shell(Shell实现版本)的代码实现,深入解析AI生成Git提交信息的核心工作流程。
AI Commits 的核心工作流程包含以下步骤:
-
变更分析
- 获取 Git 暂存区的变更(git diff —staged)
- 分析变更的文件和代码内容
-
上下文收集
- 获取最近的提交历史(默认10条)
- 提取项目的提交风格特征
-
提示词构建
-
LLM 调用
- 发送提示词到 LLM 服务
- 接收并解析生成的提交信息
-
后处理
三、实践应用指南
3.1 工具选型对比
| 功能特性 | GitHub Copilot | AI Commits | Cursor | 通义灵码 |
|---|
| 模型支持 | 固定GPT-3.5 | 可自由扩展 | 固定 Claude-3.5-sonnet | 固定 通义千问 |
| 提示词定制 | 否 | 支持 | 否 | 否 |
| 响应速度 | 快速) | 中等 | 快速 | 快速 |
| IDE 支持 | 全平台 | 仅限 JetBrains 系列 | 仅限 Cursor IDE | 全平台 |
| 订阅成本 | 需 Copilot 订阅 | 仅需模型 API 费用 | 需 Cursor Pro 订阅 | 免费 |
-
模型灵活性:支持自由扩展不同的 LLM 模型,可以根据团队需求和成本预算选择最适合的模型。
-
提示词定制:独特的提示词定制能力让团队可以统一提交规范,确保代码库的一致性。
-
成本效益:仅需支付模型 API 调用费用,相比其他工具的订阅制更具性价比(通义灵码效果堪忧)。
-
团队协作:通过统一的提示词模板和模型配置,可以确保团队成员生成风格一致的提交信息。
因此,对于重视代码提交规范、追求灵活性和可定制性的团队来说,AI Commits 是一个理想的选择。
3.2 IntelliJ AI Commits Plugin 配置指南
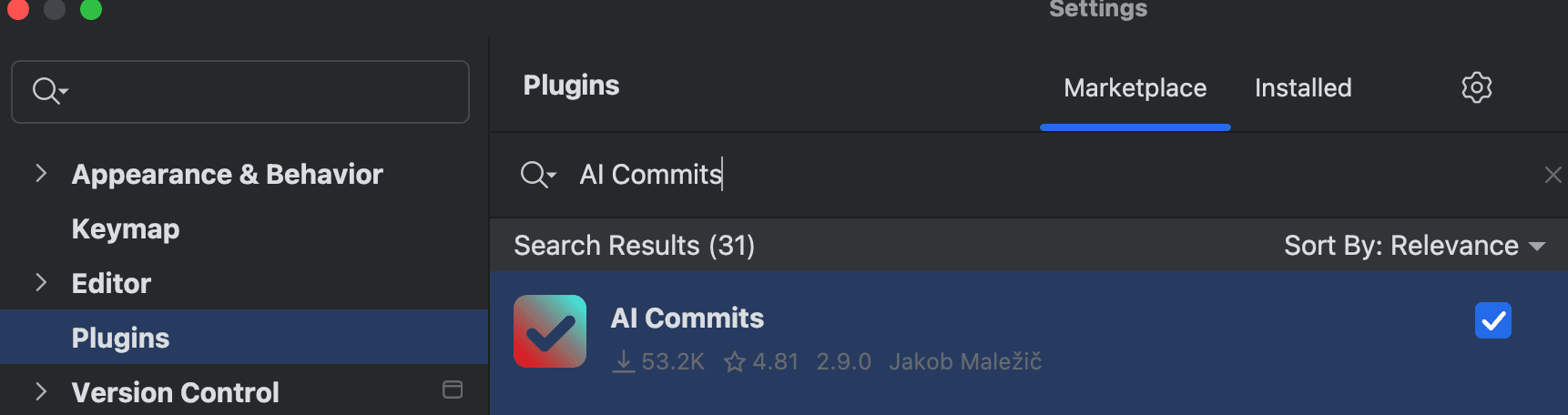
- 插件安装:
- 在 Marketplace 搜索安装
AI Commits
- 重启 IDE 激活插件
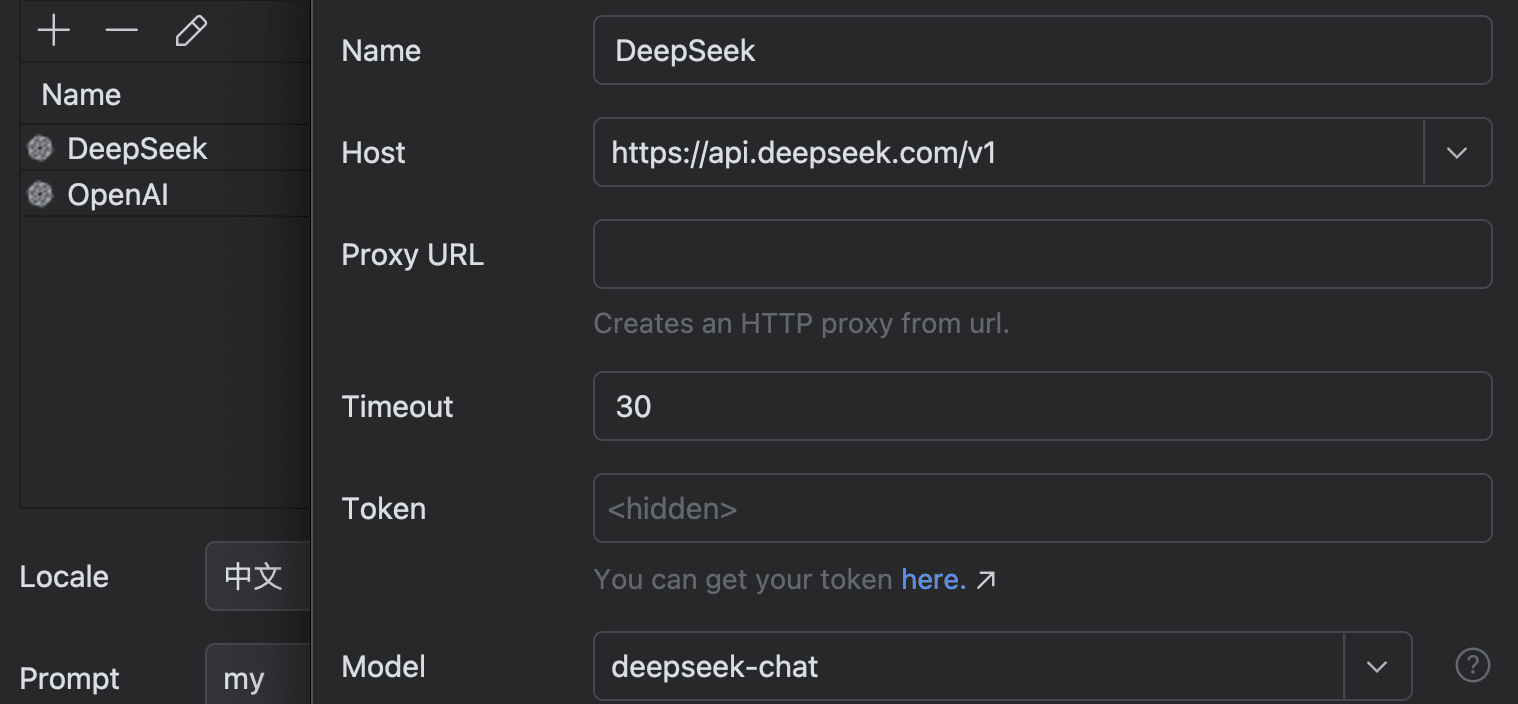
- 模型配置:
笔者测试 百炼的qwen 系列、火山的豆包系列,目前推荐的还是deepseek 的模型。
- DeepSeek-V3(性价比首选,上下文64k,足够使用,指令遵循效果好)
- Claude-3.5-Sonnet(家里有条件的,可以考虑)
3.3 提示词模板配置
Write a concise, clear, and informative commit message based on the conventional commit specification.
- Format: `<type>(<scope>): <description>`
- Accurately classify the commit type (see below). If uncertain, provide the best guess:
- feat: A new feature for the user.
- Functionality changes that are user-facing.
- fix: A bug fix.
- docs: Changes to documentation.
- style: Code style changes.
- refactor: Code changes that neither fix a bug nor add a feature;
- Only use for code changes, that do not change functionality or are user-facing.
- test: Adding or correcting tests.
- chore: Maintenance, project config or auxiliary tool changes.
- Accurately classify the commit scope (see below). If uncertain, provide the best guess:
- Noun describing a section of the codebase.
- E.g.:
areas, contacts, containers, orders, prices, settings, statistics, core, ui, config, yarn, gradle, deps,
github-actions, release.
- Use present tense and active voice.
- Subject
- Start with a lowercase letter and avoid ending with a period.
- Encapsulate any code, numbers, or filenames in backticks.
- Body (optional)
- Only add really relevant information, that are not already covered by the subject.
- If it really matters. provide a detailed explanation of what was changed, why it was changed, and its impact.
Each line, MUST NOT exceed **72** characters; Wrap in the body if necessary!
Use {locale} language to answer and not embed the response in a code block.
`git diff --staged`:
{diff}


 我们通过分析开源项目 aicommits-shell(Shell实现版本)的代码实现,深入解析AI生成Git提交信息的核心工作流程。
AI Commits 的核心工作流程包含以下步骤:
我们通过分析开源项目 aicommits-shell(Shell实现版本)的代码实现,深入解析AI生成Git提交信息的核心工作流程。
AI Commits 的核心工作流程包含以下步骤:

